CREATE Statement in Hive
HiveQL - CREATE Statement구조에 대하여
CREATE [TEMPORARY][EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
[(col_name data_type [column_constraint_specification] [COMMENT col_comment], ... [constraint_specification])]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...)
[SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
[SKEWED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) -- (Note: Available in Hive 0.10.0 and later)]
ON ((col_value, col_value, ...), (col_value, col_value, ...), ...)
[STORED AS DIRECTORIES]]
[
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
| STORED BY 'storage.handler.class.name' [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (...)] -- (Note: Available in Hive 0.6.0 and later)
]
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
[TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)] -- (Note: Available in Hive 0.6.0 and later)
[AS select_statement]
; -- (Note: Available in Hive 0.5.0 and later; not supported for external tables)
테이블을 생성하는 HiveQL은 위와 같은 포맷을 가집니다. 한줄 한줄 의미를 해석해보고자 합니다.
INTERNAL / EXTERNAL / TEMPORARY
CREATE [TEMPORARY][EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
HIVE 테이블은 크게 3가지로 생성될 수 있습니다.
1. MANAGED(Internal)
2. EXTERNAL
3. TEMPORARY
EXTERNAL, TEMPORARY는 위 쿼리에서 하나를 선택해서 입력해주면 되고, MANAGED는 아무것도 입력하지 않고 그냥 CREATE TABLE만 입력하는 경우입니다. 세 가지 테이블 형태는 어떻게 다른 것일까요.
Managed Table은 테이블(Hive)에 의해 데이터가 관리되고, External Table은 유저에 의해 데이터가 관리되어야한다는 점입니다(Hive assumes that it owns the data for managed tables. its properties and data layout will and can only be changed via Hive command. For external tables Hive assumes that it does not manage the data.)
따라서, Managed Table을 삭제하면 해당 데이터도 함께 삭제되지만, External Table은 삭제해도 테이블에 해당하는 데이터가 삭제되지 않고 Location에 남아있게됩니다. 따라서 테이블/데이터의 안전을 위해서는 External Table이 선호됩니다.
Managed tables
A managed table is stored under the hive.metastore.warehouse.dir path property, by default in a folder path similar to
/user/hive/warehouse/databasename.db/tablename/. The default location can be overridden by thelocationproperty during table creation. If a managed table or partition is dropped, the data and metadata associated with that table or partition are deleted. If the PURGE option is not specified, the data is moved to a trash folder for a defined duration.Use managed tables when Hive should manage the lifecycle of the table, or when generating temporary tables.
External tables
An external table describes the metadata / schema on external files. External table files can be accessed and managed by processes outside of Hive. External tables can access data stored in sources such as Azure Storage Volumes (ASV) or remote HDFS locations. If the structure or partitioning of an external table is changed, an MSCK REPAIR TABLE table_name statement can be used to refresh metadata information.
Use external tables when files are already present or in remote locations, and the files should remain even if the table is dropped.
Temporary Table은 View에 가깝다고 보시면 됩니다. 해당 테이블은 세션이 종료되면 함께 삭제됩니다.
A table that has been created as a temporary table will only be visible to the current session. Data will be stored in the user’s scratch directory, and deleted at the end of the session.
PARTITIONED BY
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
테이블을 파티션하여 저장합니다. 예를 들어, 파티션이 지정되지 않은 경우에는 /user/hive/warehouse/databasename.db/tablename/ 라는 하나의 디렉토리에 저장되지만, 파티션을 지정할 경우 파일들을 지정한 컬럼 기준에 따라 디렉토리에 나누어 저장하게됩니다.
Partitioned tables can be created using the PARTITIONED BY clause. A table can have one or more partition columns and a separate data directory is created for each distinct value combination in the partition columns.
PARTITIONED BY를 적용하는 경우와 적용하는 경우는 아래와 같이 저장 경로가 달라지게 됩니다.
-- PARTITIONED BY 사용 안함
CREATE TABLE page_view(viewTime INT, userid BIGINT,
page_url STRING, referrer_url STRING,
ip STRING COMMENT 'IP Address of the User')
COMMENT 'This is the page view table'
-- PARTITIONED BY(country STRING)
STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE;
-- 아래 경로에 모든 파일이 저장됩니다.
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/
-- PARTITIONED BY 사용
CREATE TABLE page_view(viewTime INT, userid BIGINT,
page_url STRING, referrer_url STRING,
ip STRING COMMENT 'IP Address of the User')
COMMENT 'This is the page view table'
PARTITIONED BY(country STRING)
STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE;
-- 아래 경로에 나누어 파일들이 저장됩니다.
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='KOR'
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='USA'
-- ...
파티션을 적용하게 되면 테이블 조회에서 성능 향상을 얻을 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 아래와 같은 쿼리를 실행한다고 가정해보면
SELECT
*
FROM
page_view
WHERE country = 'KOR';
파티션이 없는 경우에는 해당 디렉토리(/user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/) 내의 모든 파일을 조회하여야합니다. 그러나 파티션이 적용된 테이블의 경우에는 /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='KOR' 디렉토리만을 조회하면 WHERE 조건을 만족하게 됩니다. 따라서 적절한 컬럼을 선택하여 파티션해주는 것은 쿼리 성능 향상에 중요합니다.
DYNAMIC / STATIC PARTITION
파티션 테이블에 데이터 입력 시 DYNAMIC, STATIC이라는 두 가지 방법이 존재합니다.
간단하게 설명하면, DYNAMIC은 파티션 컬럼만을 지정해주면 해당 컬럼의 value에 따라 알아서 디렉토리를 생성하는 방법이고, STATIC은 해당 데이터를 저장할 디렉토리를 구체적으로 명시해주는 것입니다.
-- STATIC PARTITION
INSERT INTO TABLE page_view PARTITION (country='JPN')
SELECT *
FROM temp;
-- 아래 디렉토리가 새로 생성됩니다
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='JPN'
-- DYNAMIC PARTITION
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict; -- dynamic partition 허용
INSERT INTO TABLE page_view PARTITION (country)
SELECT *
FROM temp;
-- country value에 따라 자동으로 디렉토리를 생성합니다
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='JPN'
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='CHN'
CLUSTERED BY / SORTED BY
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...)
[SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
Bucketing과 관련된 옵션입니다. 지정된 칼럼을 해쉬 처리하여 미리 지정된 수의 파일(num_buckets)로 나누어 저장합니다. 지정된 칼럼을 기준으로 Join을 수행하는 경우에 소트 머지 버켓(SMB)으로 처리되어 성능이 향상됩니다. 파티션이 파일을 디렉토리로 나누어 저장하는 방법이라면, 버켓팅은 데이터를 파일로 나누어 저장합니다.
SORTED BY 에 의해 전달된 컬럼을 기준으로 데이터를 정렬하여 저장합니다.
CREATE TABLE page_view(viewTime INT, userid BIGINT,
page_url STRING, referrer_url STRING,
ip STRING COMMENT 'IP Address of the User')
COMMENT 'This is the page view table'
PARTITIONED BY(country STRING)
CLUSTERED BY(userid) SORTED BY(viewTime) INTO 32 BUCKETS
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\001'
COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY '\002'
MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY '\003'
STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE;
-- 아래 처럼 각 파티션 디렉토리에 num_buckets=32개의 파일로 나뉘어, viewTime 기준으로 정렬되어 저장됩니다.
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='KOR'/000000_0 ~ 000000_31
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/page_view/country='USA'/000000_0 ~ 000000_31
SKEWED BY
[SKEWED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) -- (Note: Available in Hive 0.10.0 and later)]
ON ((col_value, col_value, ...), (col_value, col_value, ...), ...)
[STORED AS DIRECTORIES]]
skewed(편향된) 데이터에 대응할 수 있는 옵션입니다. 말그대로, 어떤 컬럼에 특정 value를 가진 데이터가 많이 들어올 때 사용합니다.
This feature can be used to improve performance for tables where one or more columns have skewed values. By specifying the values that appear very often (heavy skew) Hive will split those out into separate files (or directories in case of list bucketing) automatically and take this fact into account during queries so that it can skip or include the whole file (or directory in case of list bucketing) if possible.
만약, col1이 1~100까지 값이 존재하지만, 99%의 값이 1이라면 SKEWED BY를 사용하는 것이 유리합니다. 이 경우에 PARTITIONED BY를 사용하게 되면 100개의 디렉토리를 만들지만 col1=2~col1=100까지의 파티션은 1% 데이터를 분류하기 위해 99개의 디렉토리가 생성됩니다. 반면, SKEWED BY col1 ON (1) 은 col1=1 col1!=1 2개의 디렉토리로 분류됩니다. 따라서 편향된 데이터의 경우 관리가 더 효율적입니다.
STORED AS DIRECTORIES 옵션을 지정해주면, 아래처럼 디렉토리를 따로 생성하여 저장하고, 지정하지 않으면 파일로 구분하여 저장합니다.
-- 1개 컬럼에 대해 SKEWED BY
CREATE TABLE list_bucket_single (key STRING, value STRING)
SKEWED BY (key) ON (1,5,6) [STORED AS DIRECTORIES];
-- PARTITION BY와 비슷하지만, 지정된 value에 대해서만 디렉토리를 생성하여 저장합니다.
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_single/key=1
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_single/key=5
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_single/key=6
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_single/HIVE_DEFAULT_LIST_BUCKETING_DIR_NAME
-- 2개 컬럼에 대해 SKEWED BY
CREATE TABLE list_bucket_multiple (col1 STRING, col2 int, col3 STRING)
SKEWED BY (col1, col2) ON (('s1',1), ('s3',3), ('s13',13), ('s78',78)) [STORED AS DIRECTORIES];
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_multiple/col1='s1'/col2=1
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_multiple/col1='s3'/col2=3
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_multiple/col1='s13'/col2=13
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_multiple/col1='s78'/col2=78
-- /user/hive/warehouse/default.db/list_bucket_multiple/HIVE_DEFAULT_LIST_BUCKETING_DIR_NAME
ROW FORMAT
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
구분자(delimeter), 데이터 해석 방법(SerDe)에 대한 정보를 지정합니다.
Delimeter
-- data.txt
-- a,val1^val2^val3,key1:val1^key2:val2
CREATE TABLE tbl (
col1 STRING,
col2 ARRAY<STRING>,
col3 MAP<STRING, STRING>)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',' -- Field 구분자는 ','
COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY '^' -- Collection Items 구분자는 '^'
MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY ':'; -- MAP KEYS 구분자는 :
data.txt 에 대하여 위와 같은 쿼리로 테이블을 생성하면 아래와 같은 테이블이 적재됩니다.
| a |
|---|
| {val1, val2, val3} |
| {key1:val1, key2:val2} |
SerDe
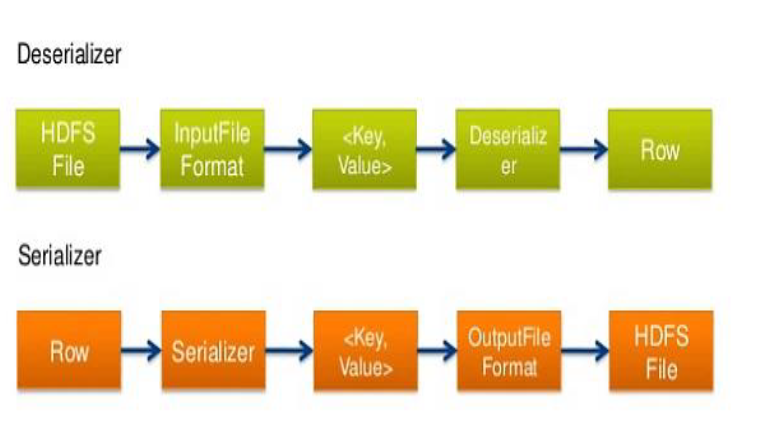
SerDe란 데이터 해석 방법을 말합니다. Serializer/Deserialaizer의 약자로 Hive가 데이터를 해석하는 방법을 제공하기 위한 수단입니다.
파일 내 데이터(HDFS Files)에 접근한 이후, 해당 데이터를 테이블로 적재하기 위해 Deserialaizer를 이용하여 Row Format으로 변환합니다. 반대로, 쿼리 결과인 Row들은 Serializer를 이용하여 파일 포맷으로 변환하여 파일로 export합니다.
-
HDFS files –> InputFileFormat –> [key, value] –> Deserializer –> Row object
-
Row object –> Serializer –> [key, value] –> OutputFileFormat –> HDFS files
-
기본 제공되는 SerDe는 다음 7개 입니다.
- Avro, ORC, RegEx, Thrift, Parquet, CSV, JsonSerDe
위 7가지 SerDe는 STORED AS 옵션에서 지정한 파일 옵션에 따라 자동으로 선택됩니다.
다음 쿼리를 통해 테이블에 지정된 SerDe를 확인할 수 있습니다.
DESC formatted orc_tbl;
SerDe Library: org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.orc.OrcSerde
InputFormat: org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.orc.OrcInputFormat
OutputFormat: org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.orc.OrcOutputFormat
기본 제공되는 7가지 SerDe, 즉 위 파일 포맷 외에 다른 형식의 파일 포맷의 데이터를 Deseiralize하여 테이블을 만들기 위해서는 Custom SerDe를 정의해야합니다.
# 데이터 확인
$ cat sample.txt
david 23!
cole 3!5
anna !92
// Custom SerDe `SampleSerDe` 정의
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.SerDeException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
// LazySimpleSerDe를 상속하여 custom SerDe를 정의
public class SampleSerDe extends LazySimpleSerDe {
public SampleSerDe() throws SerDeException {
super();
}
@Override
public Object doDeserialize(Writable field) throws SerDeException {
// 느낌표는 제거
String temp = field.toString().replaceAll("!", "");
return super.doDeserialize(new Text(temp));
}
}
Custom SerDe는 아래와 같은 방식으로 사용합니다.
# 클래스가 들어 있는 jar 파일 추가
hive> ADD JAR ./hiveUDF.jar;
# 테이블 생성 시에 서데 정보 및 프로퍼티 정보 전달
hive> CREATE TABLE serde_tbl
(
col1 STRING
, col2 STRING
)
ROW FORMAT SERDE 'com.sec.hive.serde.SampleSerDe'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ( "field.delim" = "\t" )
;
# 샘플 데이터를 입력
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH './sample.txt' INTO TABLE serde_tbl;
# 데이터 조회
hive> select * from serde_tbl;
OK
david 23
cole 35
anna 92
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES는 SerDe에서 지정되지 않은 구분자를 추가해줍니다.
ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (
'serialization.format' = ',',
'field.delim' = ',',
'collection.delim' = '|',
'mapkey.delim' = ':',
'escape.delim' = '\\'
)
STORED AS
[STORED AS file_format]
기본적으로 아래 7가지 format을 제공합니다. 아래 file format은 SerDe도 함께 제공됩니다.
| Storage Format | Description |
|---|---|
| STORED AS TEXTFILE | Stored as plain text files. TEXTFILE is the default file format, unless the configuration parameter hive.default.fileformat has a different setting.Use the DELIMITED clause to read delimited files.Enable escaping for the delimiter characters by using the ‘ESCAPED BY’ clause (such as ESCAPED BY ‘') Escaping is needed if you want to work with data that can contain these delimiter characters. A custom NULL format can also be specified using the ‘NULL DEFINED AS’ clause (default is ‘\N’). (Hive 4.0) All BINARY columns in the table are assumed to be base64 encoded. To read the data as raw bytes:TBLPROPERTIES (“hive.serialization.decode.binary.as.base64”=”false”) |
| STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE | Stored as compressed Sequence File. |
| STORED AS ORC | Stored as ORC file format. Supports ACID Transactions & Cost-based Optimizer (CBO). Stores column-level metadata. |
| STORED AS PARQUET | Stored as Parquet format for the Parquet columnar storage format in Hive 0.13.0 and later; Use ROW FORMAT SERDE … STORED AS INPUTFORMAT … OUTPUTFORMAT syntax … in Hive 0.10, 0.11, or 0.12. |
| STORED AS AVRO | Stored as Avro format in Hive 0.14.0 and later (see Avro SerDe). |
| STORED AS RCFILE | Stored as Record Columnar File format. |
| STORED AS JSONFILE | Stored as Json file format in Hive 4.0.0 and later. |
STORED AS INPUTFORMAT/OUTPUTFORMAT
in the file_format to specify the name of a corresponding InputFormat and OutputFormat class as a string literal. For example, ‘org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.fileformat.base64.Base64TextInputFormat’. For LZO compression, the values to use are ‘INPUTFORMAT “com.hadoop.mapred.DeprecatedLzoTextInputFormat” OUTPUTFORMAT “org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat”’ (see LZO Compression).
INPUTFORMAT과 OUTPUTFORMAT을 따로 지정해줄 수도 있습니다.
-- INPUTFORMAT, OUTPUTFORMAT을 따로 지정하는 것도 가능
CREATE TABLE tbl1 (
col1 STRING
) STORED AS INPUTFORMAT "com.hadoop.mapred.DeprecatedLzoTextInputFormat"
OUTPUTFORMAT "org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat";
STORED BY
STORED BY 'storage.handler.class.name'
Stored by a non-native table format. To create or link to a non-native table, for example a table backed by HBase or Druid or Accumulo. See StorageHandlers for more information on this option.
non-native table 은 Hive에 의해 저장되지 않은 데이터 소스로부터 생성된 테이블을 의미합니다. 이들은 각각의 data source에 알맞은 handler를 적용해야합니다 (Tables that use a storage handler, such as the DruidStorageHandler or HBaseStorageHandler).
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE hiveTableName
(col1 string, col2 bigint, col3 array<string>)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.dynamodb.DynamoDBStorageHandler'
TBLPROPERTIES ("dynamodb.table.name" = "dynamodbtable1",
"dynamodb.column.mapping" = "col1:name,col2:year,col3:holidays");
위 쿼리는 DynamoDB에 저장된 데이터를 참조하는 Hive 테이블을 만듭니다.
LOCATION
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
LOCATION now refers to the default directory for external tables and MANAGEDLOCATION refers to the default directory for managed tables. Its recommended that MANAGEDLOCATION be within metastore.warehouse.dir so all managed tables have a common root where common governance policies. It can be used with metastore.warehouse.tenant.colocation to have it point to a directory outside the warehouse root directory to have a tenant based common root where quotas and other policies can be set.
Managed Table은 default deirctory(MANAGEDLOCATION)에 데이터를 저장하므로 LOCATION을 명시하지 않습니다. 해당 옵션은 EXTERNAL Table에서 데이터의 위치를 전달하기 위해 사용됩니다.
The EXTERNAL keyword lets you create a table and provide a LOCATION so that Hive does not use a default location for this table. This comes in handy if you already have data generated.
External Table은 DROP 시, 테이블은 삭제되지만 LOCATION의 데이터들은 삭제되지 않습니다. 테이블 삭제와 동시에 데이터도 삭제하기 위해서는 아래 따로 옵션을 지정해주어야합니다(setting table property external.table.purge=true, will also delete the data).
TBLPROPERTIES
[TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)]
테이블 속성(옵션)을 지정해줍니다. 아래와 같은 옵션들이 존재합니다.
The TBLPROPERTIES clause allows you to tag the table definition with your own metadata key/value pairs. Some predefined table properties also exist, such as last_modified_user and last_modified_time which are automatically added and managed by Hive. Other predefined table properties include:
- TBLPROPERTIES (“comment”=”table_comment”)
- TBLPROPERTIES (“hbase.table.name”=”table_name”) – see HBase Integration.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“immutable”=”true”) or (“immutable”=”false”) in release 0.13.0+ (HIVE-6406) – see Inserting Data into Hive Tables from Queries.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“orc.compress”=”ZLIB”) or (“orc.compress”=”SNAPPY”) or (“orc.compress”=”NONE”) and other ORC properties – see ORC Files.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“transactional”=”true”) or (“transactional”=”false”) in release 0.14.0+, the default is “false” – see Hive Transactions.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“NO_AUTO_COMPACTION”=”true”) or (“NO_AUTO_COMPACTION”=”false”), the default is “false” – see Hive Transactions.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“compactor.mapreduce.map.memory.mb”=”mapper_memory”) – see Hive Transactions.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.num.threshold”=”threshold_num”) – see Hive Transactions.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“compactorthreshold.hive.compactor.delta.pct.threshold”=”threshold_pct”) – see Hive Transactions.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“auto.purge”=”true”) or (“auto.purge”=”false”) in release 1.2.0+ (HIVE-9118) – see Drop Table, Drop Partitions, Truncate Table, and Insert Overwrite.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“EXTERNAL”=”TRUE”) in release 0.6.0+ (HIVE-1329) – Change a managed table to an external table and vice versa for “FALSE”.
- As of Hive 2.4.0 (HIVE-16324) the value of the property ‘EXTERNAL’ is parsed as a boolean (case insensitive true or false) instead of a case sensitive string comparison.
- TBLPROPERTIES (“external.table.purge”=”true”) in release 4.0.0+ (HIVE-19981) when set on external table would delete the data as well.
AS SELECT
[AS select_statement]
CTAS(CREATE-TABLE-AS-SELECT) 구문에서 사용됩니다. 해당 구문으로 생성하고자하는 테이블은 CTAS 쿼리가 완료되기 전까지는 다른 유저에 의해 조회가 불가능합니다.
Tables can also be created and populated by the results of a query in one create-table-as-select (CTAS) statement. The table created by CTAS is atomic, meaning that the table is not seen by other users until all the query results are populated. So other users will either see the table with the complete results of the query or will not see the table at all.
아래와 같은 형식으로 사용됩니다.
CREATE TABLE new_key_value_store
ROW FORMAT SERDE "org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.columnar.ColumnarSerDe"
STORED AS RCFile
AS
SELECT (key % 1024) new_key, concat(key, value) key_value_pair
FROM key_value_store
SORT BY new_key, key_value_pair;
CTAS 구문은 몇 가지 특징을 갖습니다. 하나씩 살펴보면 아래와 같습니다.
- CTAS구문 사용 시, External Table을 생성할 수 없고, Bucket도 지정할 수 없습니다.
CTAS has these restrictions:
- The target table cannot be an external table.
- The target table cannot be a list bucketing table.
- Source Table(SELECT 구문 안의 테이블)과 별개의 SerDe와 File Format을 지정할 수 있습니다. 즉, 위 쿼리에서
new_key_value_store의 File Format과 SerDe는key_value_store와 동일하지 않아도 됩니다.
the new target table is created using a specific SerDe and a storage format independent of the source tables in the SELECT statement.
- CTAS 구문은 CTE(Common Table Expression)과 함께 사용될 수 있습니다.
CREATE TABLE s2 AS
WITH q1 as ( select key from src where key = '4') -- CTE
SELECT * FROM q1;
여기까지, Hive CREATE TABLE에서 사용되는 쿼리에 대해서 모두 살펴보았습니다. 가장 중요한 부분은 Partition, Bucket , Skew 부분이 아닌가 싶습니다. 처음 HiveQL를 접하시는 분들께 이 포스팅이 도움이 되었으면 좋겠습니다.
[참조]